Technology that could transform medicine. Algae nanobots
Nanobots designed to traverse the insides of the human body are one of the most promising technologies for future medicine. Thanks to Chinese scientists, we are one step closer to reaching our goal. Their device built from algae solves some problems with technical.
Engineers over decades of pr bowali to build microscopic medical robots, which re could deliver drugs directly to the site of infection or perform surgery inside the body. Despite considerable progress in the field to use this type of nanobot still a long way to go, though we are one step closer to realizing the goal.
Although the technology has the potential to change our lives, its use is still limited. There are several problems waiting to be solved In connection with powering these tiny devices and guiding them through the body. A step in this direction was taken by the team Chinese scientists under the direction of Li Zhang of the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
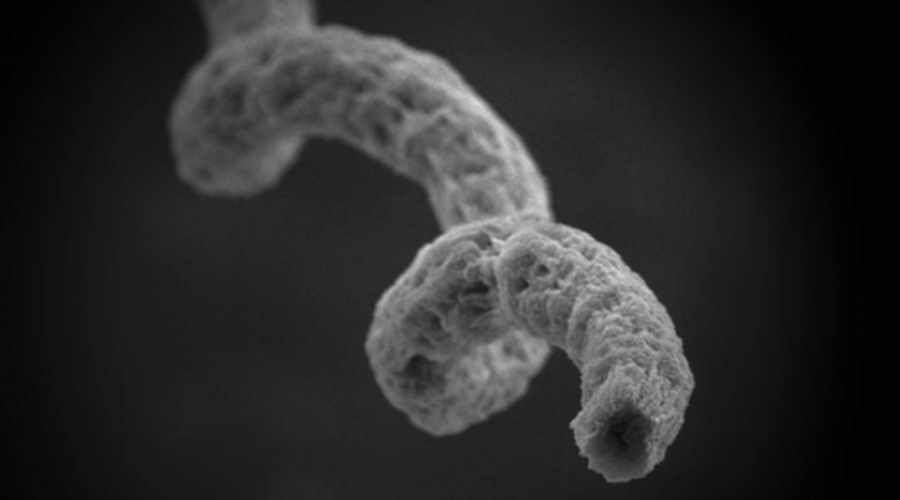
In a study published in the journal „Science Robotics”, Zhang and his co he researchers have demonstrated a prototype technology based on the algae Spirulina platensis, which re look like a microscopic spring. They are commonly used as a dietary supplement. Chinese researchers have manipulated spirulina so that it can move freely inside the human body in response to magnetic signals.
Finding the right power for nanobots was quite a challenge, since most potential fuels are toxic to the body. Another problem was controlling such a small robot through the labyrinths inside our bodies, which requires zar or a way to control its movement , as well as checking where they are located. But it seems that both of these problems have been solved.
A few years ago, composite ł Zhang created the nanobot inspired by the shape of algae, now he has used the algae itself for his purposes. The key lies in magnetizing the algae by coating them with iron oxide nanoparticles. Magnetic fields generated outside the body can without obstruction d penetrate living tissue, allowing researchers to move magnetized objects. On top of that, these algae are fluorescent, which allows them to be tracked by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
– Tracking nanobots The development of a new solution in the body is a big step forward d. In addition, the technology developed is cheap and biocompatible – said Joseph Wang of the University of California San Diego, who ry has been working on a similar solution for years.
The biocompatibility mentioned by Wang is an important feature of the. Nanobot developed by the team ł Zhang degrades within a few hours or days, depending on the thickness of the applied iron oxide layer, and does not make any major damage d in the body.
Syndrome ł Zhang observed another surprising feature of the developed technology. During the experiments, 90 percent of the. com tumor rec growing in a laboratory dish was destroyed after exposure to iron oxide-coated spirulina. Further testing showed that this algae produces a compound toxic only to com cancer records.
However, for the introduction of nanobots There is still a long way to go. syndrome Zhang’s ł must demonstrate that the nanobot they developed is capable of carrying a payload In the case of medicines, for example.


