
Rubber ducks for bathing are a paradise for pathogens
In our daily lives, we are surrounded at every turn by traps that can cause disease, and objects that re we associate with cleaning, they are in fact a haven for pathogens. For example, a dishwashing sponge, which is found in almost every home, already after a short a short time of use contains millions of microbes , including close relatives of bacteria that The results of their research have been published in the journal zgowych. Read more here: Kitchen sponge may harbor dangerous bacteria.
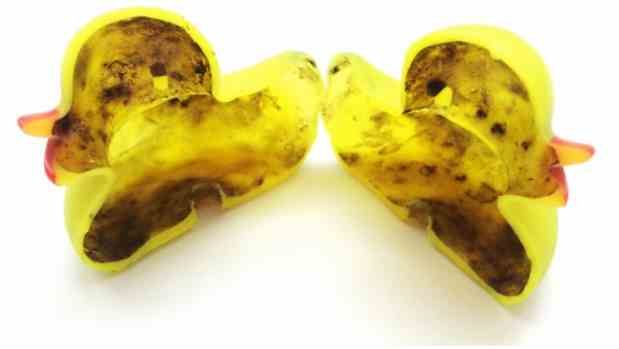
The same is true of rubber duckies for bathing. For the he seemingly friendly facade hides a dirty, potentially dangerous secret. Inside rubber ducks there is a dream environment for bacteria and fungi , which re can cause disease.
US and Swiss scientists report The findings are worrisome, as these toys are used by the youngest children. Rubber ducks are something we associate with happiness, laughter and innocence. Children play with them, squeeze water out of them, even put them in their mouths.
Warm, humid bathrooms provide ideal conditions for bacterial and fungal growth – for example, on shower curtains or behind cabinets. This applies in particular to larity of rubber ducks and other bath toys.
In a new study, researchers from the Swiss Federal Institute of Water Science and Technology and (eawag) from the University of Illinois analyzed 19 rubber bath ducks obtained from Swiss households. For the six new toys, they mimicked real conditions by exposing them to clean and dirty bath water mixed with soap. The rubber ducks, crocodiles and other bath toys remained clean unfortunately only for kr tki period. The results of their research were published in the journal „Biofilms and Microbiomes”.
After 11 weeks of simulated home use, all the toys were cut in two in the lab, revealing the biofilm lining their inner surfaces. However, the composition of biological environments was very zr gnicated, especially lnie among d bath toys from real households, as well as between the two control groups.
R trong species of fungi were detected in most bath toys exposed to dirty water, and potentially dangerous bacteria were found in 80 percent of all toys. Among d them were found m.In. legionella bacteria – causing severe infectious disease of dr g respiratory or blue pus bacilli – often associated with hospital-acquired infections.
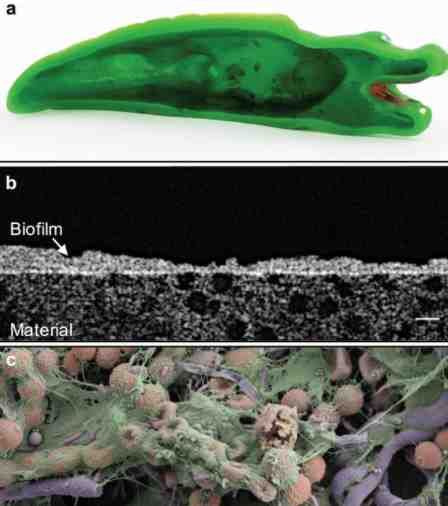
The presence of some rych bacteria and fungus inside the toys depended on the quality of the water or the material they were made of. Low-quality polymers release significant amounts of organic compounds in coal, which ry is a breeding ground for bacteria. Tap water, on the other hand, is usually not conducive to microbial growth .
Other key nutrients for bacteria, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as additional bacteria, are provided by the human body (body fluids – urine and sweat) during the bath itself. Added to this are external contaminants and personal hygiene products.
According to microbiologist Frederik Hammes, exposures to such microorganisms may have zar both positive and negative effects. – Such contact may strengthen the immune system, which would be a positive effect, but may nly cause infections of the eyes, ears and even the digestive tract – admitted the researcher. – Moldy bath toys are widely commented on online forums and blogs, but so far little scientific attention has been paid to them – added.
Scientists say more research is needed to rule conclusively on what effect such pathogens can have on children’s bodies. They also advise regularly cleaning toys after bathing by boiling and drying them, to minimize the risk of microbes colonizing them.


