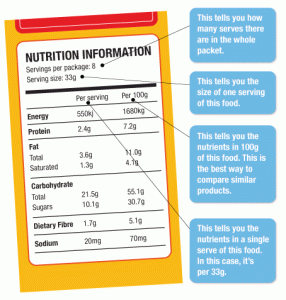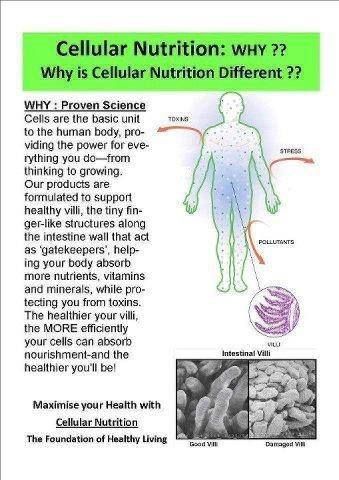
In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining good health has become more important than ever. With increasing stress levels and sedentary lifestyles, it is crucial to understand the role of nutrients in cellular health. Our cells are the building blocks of life, and keeping them healthy is essential for overall well-being. This article delves into the significance of various nutrients and how they contribute to cellular health.
The Importance of Nutrients for Cellular Health
Nutrients are substances that provide the necessary building blocks and energy for cellular processes. They play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and proper functioning of our cells. Without adequate nutrients, cells may become weak, leading to various health issues.
1. Proteins
Proteins are essential macronutrients that play a vital role in cellular health. They are responsible for cell growth, repair, and maintenance. Proteins are composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of our cells.
2. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy for cellular processes. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels the cells. Glucose is essential for brain functioning and provides energy for various metabolic activities.
3. Fats
Fats are often misunderstood as harmful substances. However, healthy fats are crucial for cellular health. They provide insulation, protection, and act as a reserve source of energy for the cells. Fats also aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, which are essential for cellular processes.
4. Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients that play a key role in cellular health. They support numerous cellular functions, including enzyme activation, energy production, and cell communication. Different vitamins and minerals have specific roles, and an adequate intake is necessary for optimal cellular health.
Effects of Nutrient Deficiencies
When our cells do not receive sufficient nutrients, their functionality is compromised. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to various health issues and impair cellular processes.
1. Protein Deficiency
Inadequate protein intake can result in weakened cell repair and maintenance. It can lead to muscle wasting, compromised immune function, and delayed wound healing.
2. Carbohydrate Deficiency
Insufficient carbohydrate intake can deprive cells of their primary energy source, leading to fatigue, weakness, and impaired brain function. Prolonged carbohydrate deficiency can also cause muscle breakdown as the body looks for alternative energy sources.
3. Fat Deficiency
A lack of healthy fats can impair cellular function, as they are crucial for insulation, protection, and energy reserve. It may result in dry skin, weakened immune system, and hormonal imbalances.
4. Vitamin and Mineral Deficiency
Inadequate intake of vitamins and minerals can disrupt various cellular processes. Deficiencies in specific nutrients may lead to weakened immune system, impaired nerve function, reduced energy production, and a higher susceptibility to diseases.
Conclusion
It is evident that nutrients play a vital role in maintaining cellular health. Proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals provide the necessary building blocks, energy, and support for our cells to function optimally. A well-balanced diet, rich in these essential nutrients, is crucial for promoting cellular health and overall well-being. So, let’s be mindful of our nutrient intake and ensure we provide our cells with the fuel they need to thrive.