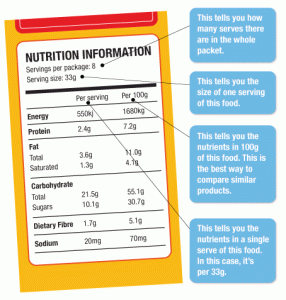
Proper nutrition is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. Our bodies require a variety of nutrients to function optimally, including macronutrients and micronutrients. Understanding the difference between these two types of nutrients is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the nutrients that our bodies need in larger amounts to provide energy and support growth, development, and overall health. The three main macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They consist of sugars, starches, and fibers, which are broken down into glucose to fuel our cells. While carbohydrates often have a bad reputation, they are essential for proper bodily functions. Good sources of carbohydrates include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
Proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of our body, responsible for repairing tissues, supporting growth, and creating hormones and enzymes. They are made up of amino acids, which are essential for various bodily functions. Good sources of protein include animal products, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy, as well as plant-based sources like legumes, tofu, and quinoa.
Fats
Fats are often misunderstood, but they play a vital role in our health. They provide energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and help our bodies absorb certain nutrients. There are different types of fats, including saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and trans fats. While saturated and trans fats can be harmful in excess, unsaturated fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, avocado, and olive oil, provide numerous health benefits.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are the nutrients that our bodies need in smaller amounts but are just as important as macronutrients. These include vitamins and minerals, which are essential for various bodily functions, including immune system support, bone health, and energy production.
Vitamins
Vitamins are organic compounds that help our bodies regulate various processes. They can be divided into two categories: water-soluble vitamins (such as vitamin C and B vitamins) and fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K). Each vitamin has specific functions and can be obtained from a diverse range of food sources.
Minerals
Minerals are inorganic substances that our bodies need in small amounts. They are involved in several bodily functions, including bone health, nerve transmission, and enzyme function. Common minerals include calcium, potassium, iron, and zinc. Eating a varied diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help meet your mineral needs.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Both macronutrients and micronutrients play crucial roles in our overall health, and it is important to consume them in appropriate quantities. A balanced diet that incorporates a variety of foods from all food groups is essential to ensure we get an optimal intake of all required nutrients.
When planning your meals, aim for a combination of whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. This will help provide you with the necessary macronutrients and ensure sufficient intake of various vitamins and minerals.
It’s worth noting that individual nutrient needs can vary based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and specific health conditions. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to your unique needs.
Conclusion
Understanding macronutrients and micronutrients is key to maintaining proper nutrition and overall health. While macronutrients provide energy and support growth, micronutrients are necessary for various bodily functions. By consuming a balanced diet that incorporates a wide range of food sources, we can ensure we meet our nutrient needs and promote optimal well-being.